The corneal dystrophies are a large group of disorders that involve the dysfunction of the corneal metabolic processes. This leads to an accumulation of various substances within the cornea, which ultimately obstruct vision. The disorders are typically characterised by anatomical location and are discussed in detail on this page.
You need not learn all of these in detail, but make sure you are aware of Fuchs endothelial dystrophy for the exam.
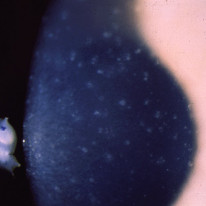
Epithelial Dystrophies
Cogan (epithelial basement membrane)
- The commonest corneal epithelial dystrophy
- Isolated cases with no family history
- Histology shows a thickened basement membrane over Bowman's layer
- Retroillumination on slit-lamp shows: map-like subepithelial opacities, fingerprint-like subepithelial ridges, and dot-like intraepithelial cysts
Meesmann (epithelial)
- Non-progressive abnormality of epithelial metabolism
- AD inheritance, KRT3/KRT12 mutation
- Histology shows cysts
- Treatment involves lubrication
Bowman's/Anterior Stromal
Reis-Bucklers
- This is an anterior variant of granular stromal dystrophy (GCD 3) and is also known as CBD1
- AD inheritance with TGFBI gene defect
- Histology shows replacement of Bowman's layer by connective bands
Thiel-Behnke dystrophy, also known as CBD2, is essentially a less severe CBD1. It is also AD inheritance with TGFBI defect.
Stromal Dystrophies
Inheritance |
Histology |
|
|---|---|---|
Lattice dystrophy TGFBI type |
This is the classic form of lattice dystrophy AD inheritance TGFBI |
Histology shows amyloid with Congo red |
Meretoja syndrome |
Can look like lattice dystrophy but is a systemic condition with associated neuropathies AD inheritance GSN |
Histology shows amyloid with Congo red |
Granular dystrophy type 1 |
AD TGFBI |
Histology shows hyaline deposits staining bright red with Masson trichrome |
Granular dystrophy type 2 |
AD TGFBI |
Histology shows hyaline and amyloid |
Macular |
CHST6 |
Aggregations of glycosaminoglycans |
Schnyder (crystalline) |
UBIAD1 |
Phospholipid and cholesterol deposits |
Important stromal dystrophies and associated lesions/stains are commonly remembered by the mnemonic: Marilyn Monroe Always Gets Her Men in L. A. County'
'Marylin Monroe Always' : Macular dystrophy - Mucopolysaccharide - Alcian blue
'Gets Her Men' : Granular dystrophy - Hyaline materials - Masson trichrome
'L. A. County' : Lattice dystrophy - Amyloid - Congo red
Fuchs Endothelial Dystrophy
The most common corneal dystrophy overall.
Pathology
- Failure of sodium-potassium pump in corneal endothelium leads to fluid accumulation and endothelial cell loss
- Corneal oedema can be exacerbated post eye surgery e.g post-cataract extraction.
Diagnostics
Presentations
- Typical presentation is an elderly woman with blurry vision worse in the morning, clearing towards the end of the day
Investigations
- Slit-lamp examination can show a beaten metal appearance of the endothelium → represents the characteristic clinical sign of corneal guttata
- The cornea will also be thicker when measured on pachymetry
- Specular microscopy can show dark spots as evidence of endothelial cell loss.
Symptoms are worse in the morning because the eyes are shut overnight and corneal fluid evaporation is limited. The endothelial pump is dysfunctional so fluid accumulation occurs. Throughout the day the eyes are open and blinking, this allows for better clearing of the accumulated fluid.
Management
- Topical sodium chloride drops and hairdryer application can help relieve symptoms
- Posterior lamellar keratoplasties (i.e., DMEK & DSAEK) can be used to treat severe disease