These are cancers of the skin which present on the eyelid. There are 4 important ones you should be aware of and they are discussed in this section in order of commonality.
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
By far the commonest cancer in ophthalmology.
Presentation
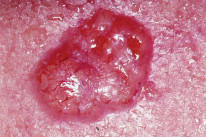
- Most commonly occurs on lower lid of eye and upper lip of the mouth.
- It is a slow-growing lesion and does not typically spread.
- The lesion is pearly white with associated telangiectasia.
Management
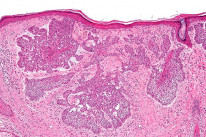
- Surgical resection.
- Mohs Micrographic surgery can be used in high-risk cases where the lesion margins are uncertain.
Vismodegib is a medication approved for non-resectable cases and works through the Hedgehog pathway. BCC is associated with Ptch/Smo gene mutation in the Hedgehog pathway.
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
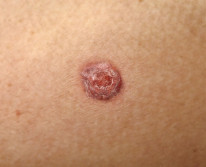
The second most common malignant eyelid tumour. Associated with HPV infection, ultraviolet light exposure, and immunocompromise.
Pathology
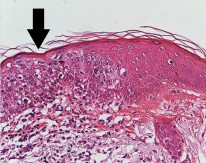
- Aggressive and spreads via lymphatics.
- Histology shows epidermal proliferation, atypical keratinocytes, and squamous eddies.
Management
- Surgical excision, radiotherapy, chemotherapy.
Melanoma
Melanoma is not always pigmented.
Pathology
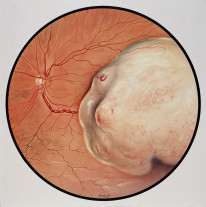
- Eyelid melanomas arise from melanocytes in the skin.
- Ocular melanomas most commonly arise from the choroid (highest concentration of melanin).
- Cutaneous melanomas spread to regional lymph nodes, while choroidal melanomas typically spread to the liver.
- Breslow thickness is the prognostic indicator for cutaneous melanomas.
Management
- Surgical excision, radiotherapy, chemotherapy.
Vemurafenib is a kinase inhibitor with FDA approval for unresectable tumours with BRAF V600E mutation.
Sebaceous Gland Carcinoma
Sebaceous gland carcinoma arises from Meibomian and Zeis glands.
Pathology
- Can be misdiagnosed as unilateral blepharitis. Blepharitis is seldom unilateral.
- Spreads to lymph nodes and viscera.
- Associated with Muir-Torre syndrome.
Management
- Surgical excision, radiotherapy, chemotherapy.
- Prognosis is poor.

