Paediatric leukocoria is a white pupil or absence of a red reflex during the examination. It can be caused by: congenital cataract, retinoblastoma, persistent fetal vasculature, retinopathy of prematurity, Coats disease, and toxocariasis. The conditions that are not covered on this page are reviewed elsewhere.
Retinoblastoma
-
Most common primary intraocular malignancy in children
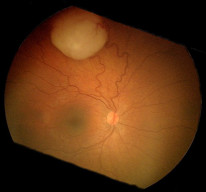
Fundus photograph of a patient with retinoblastoma. By Tero Kivelä, CC BY 2.5. -
Arises from photoreceptor cells
-
Associated with RB1 mutation on chromosome 13.
-
Most commonly sporadic but can be autosomal dominant
-
Histopathology classically shows Flexner rosettes
-
Presentation: Typically 3-year-old child with leukocoria (often unilateral), strabismus, decreased visual acuity, white round mass in fundus, and calcification visible on ultrasound
-
Management is typically with enucleation
Persistent Fetal Vasculature

- Also known as Persistent hyperplastic primary vitreous
- It is the failure of embryonic hyaloid artery regression.
- Presentation: 2-week-old premature infant with unilateral leukocoria, microphthalmia, and Mittendorf's dot
Mittendorf's dot is an examination finding of a posterior lens capsule opacity. Bergmeister's papilla is similar, but it arises from the optic disc. Both of these findings are related to the hyaloid artery
Retinopathy of Prematurity
A retinal disease caused by oxygen therapy in premature infants
Pathology

- In utero, retinal vascular growth is driven by a relatively hypoxic state.
- When premature infants are given oxygen therapy, the retinal vessels become disorganised and scarred. This can lead to retinal detachment and loss of vision
- Retinal vessels reach the nasal ora serrata at 32 weeks and temporal serrata at 40 weeks. This means that the temporal retina is first affected because it is much weaker.
Zone Classification
- Zone 1: Radius twice the distance from disc to fovea with the disc at the centre
- Zone 2: From the edge of Zone 1 to nasal ora serrata
- Zone 3: From Zone 2 to the remaining retina
Staging
- White line demarcating avascular areas
- Elevated thicker line
- Extra retinal fibrovascular proliferation or neovascularization of the vitreous
- Partial retinal detachment
- Total retinal detachment
- Plus disease: Signs of vessel dilation or tortuosity
Diagnostics
Presentation
- Premature infant + <1500g + birth hypoxia
Diagnostics
- Screening: High-risk infants with indirect ophthalmoscopy using a 28D lens.
- All infants <32 weeks gestation or <1500g are high risk
- If born <27 weeks gestation: Screen at 30 weeks postmenstrual age
- If born 27-32 weeks OR > 32 weeks + <1500g: Screen at 4 weeks postnatal age
- Stage 3 OR plus disease: Screen weekly
- Otherwise: Screen every 2 weeks
Recall from the lens chapter that indirect ophthalmoscopy allows the examiner to visualise up to the peripheral edges of the retina, to ensure lesions are not missed.
Management
- Transpupillary diode laser treatment within 48 hours

