Inflammation of the cornea can manifest in several specific ways that are distinct from infective keratitis. These manifestations are reviewed on this page.
Interstitial Keratitis (IK)
Interstitial keratitis is an inflammation of the corneal stroma. There are many causes of IK and the high-yield ones are discussed in this section.
Pathology
- Inflammation of the corneal stroma in the absence of primary epithelial or endothelial involvement.
- Over time, this inflammation leads to scarring which looks feather-like and has associated ghost vessels.
Causes
Disease |
Key Features |
|---|---|
Syphilitic IK |
|
Cogan Syndrome |
|
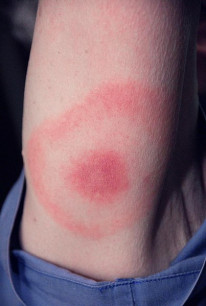
Lyme Disease |
|
Peripheral Ulcerative Keratitis (PUK)
Inflammation around the corneal circumference rather than the central cornea is characteristic of some important corneal and extra-corneal diseases.
Pathology
- Inflammation/ulceration progresses centrally and posteriorly in most cases.
- PUK is typically either caused by infection or a systemic autoimmune disorder.
In practice, PUK is caused by infection until proven otherwise. Finding PUK in isolation, in the absence of other ocular pathology is suggestive of a systemic autoimmune disorder.
Systemic Autoimmune Associations
- Rheumatoid arthritis - the most common systemic autoimmune cause of PUK.
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA).
- Crohn's disease.
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE).
- Polyarteritis nodosa.
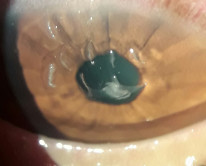
Filamentary Keratitis
A common condition caused by mucous and strand adhesion to the corneal surface due to degenerations of the corneal epithelium. It can cause severe discomfort.
Diagnostics
Presentation
- Typically found in cases of abnormal tear film such as dry eye, LASIK and contact lens wearers.
- Patients present with watery, irritated red eye with a foreign body sensation.
Investigations
- Rose bengal staining of the corneal surface shows comma-shaped lesions which move whilst blinking.
Management
- Mucolytics such as acetylcysteine drops.
- NSAID drops to address discomfort.
Mooren Ulcer
Mooren ulcer is a distinctive peripheral corneal disorder caused by autoimmune stromal ulceration.
Diagnostics
Presentation
- Pain, photophobia and blurry vision.
- Characteristic peripheral corneal ulcer with an undefined edge.
Management
- Immunomodulation with steroids.
- Oral tetracyclines can be used for their anti-collagenase effects.

