The cornea is an important structure involved in the focusing of light onto the retina. Disorders of the cornea are serious and can be sight-threatening.
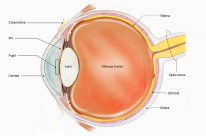
Anatomy and Physiology
The cornea (45D) has the highest refractive power of the eye, and in addition to focusing light, it also filters out UV rays.
Anatomy
- 10.6mm vertical length and 11.7mm horizontal length.
- 7.8mm anterior curvature and 6.5mm posterior curvature.
- Thickness = 555µm in the centre, thicker at the periphery.
- Dermatan sulphate and keratan sulphate are found in the stroma.
- Avascular immune-privileged structure (lacks MHC II cells).
- Innervated by CNV1 via long ciliary nerves.
Layers of the cornea (superficial to deep)

- Epithelium: stratified non-keratinised squamous epithelium.
- Bowman's layer.
- Stroma: thickest layer, and contains collagen type 1.
- Descemet's membrane: contains collagen type 4.
- Endothelium: maintains corneal transparency by mitochondrial pumping of water from stroma to aqueous.
Palisades of Vogt are radial folds of the cornea at the superior and inferior limbus (the boundary between the cornea and sclera).
Endothelial cell density < 800 cells/mm² is considered to be corneal endothelial failure.
Corneal endothelial donors must have >1500 cells/mm² density.
Special Tests
Specular microscopy

- Used to study the corneal endothelium at high resolution.
- Corneal endothelial cells are hexagonal and the normal adult has a cell density of around 3000 cells/mm².
- The number of corneal endothelial cells decrease with age.
- Highest endothelial cell density is at the periphery.
The normal range for corneal endothelial cell density is 1500-3500 cells/mm².
Corneal Topography
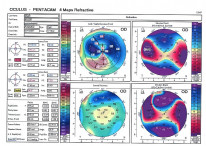
- Produces an image of the shape of the corneal surface.
- Principally used in the evaluation of corneal ectasias and astigmatism.
- This is further discussed in the refraction chapter.
Pachymetry and OCT are used to measure corneal thickness.
Fluorescein Staining
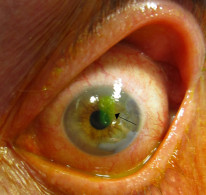
- Used in the identification of corneal epithelial lesions.
- Corneal epithelial defects stain green with fluorescein.
Management Overview
Epithelial defects
- May require re-epithelialization to promote healing.
- Lubrication with artificial tears.
- Bandage contact lenses.
- PO doxycycline.
Persistent unresponsive epithelial defects:
- Amniotic membrane graft.
- Autologous serum drops.
Doxycycline is a matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) inhibitor which promotes wound healing.
Exposure/neurotrophic keratopathy
Management involves closing the lids through:
- Taping of the lids.
- Botox to the levator muscle.
- Gold weight upper lid insertion for facial nerve palsy.
- Tarsorrhaphy.
Smoking hinders epithelial healing and should be stopped.
Limbal stem cell deficiency
- Limbal stem cell transplantation.
The Palisades of Vogt can be lost in cases of limbal stem-cell failure.
Dry eye
- Artificial tears and lubricants.
- Punctal plugs.
Keratoplasty
Keratoplasty (corneal transplant), can be full-thickness (penetrating) or partial thickness (anterior or posterior lamellar).
Indications
- Optical - keratoconus (commonest), scarring, corneal dystrophies, bullous keratopathy.
- Therapeutic - removal of infected corneal tissue.
Types of Keratoplasty
Type |
Description |
Indication |
|---|---|---|
Penetrating keratoplasty (PKP) |
Donor transplantation of the full thickness of the cornea. They are usually stitched with non-dissolvable stitches so PKP eyes look distinctive |
|
Tectonic Lamellar Patch |
This is a full-thickness small patch of cornea used to plug a perforation until eye the becomes quiet. Then do full PKP |
|
Deep anterior lamellar keratoplasty (DALK) |
Partial-thickness transplant of the anterior cornea to the level of Descemet's membrane Because the endothelium isn’t transplanted, lower risk of rejection compared to PKP |
|
Descemet's stripping automated endothelial keratoplasty (DSAEK) |
An endothelial keratoplasty which replaces Descemet's and endothelium. It also adds stroma. |
|
Descemet's membrane endothelial keratoplasty (DMEK) |
An endothelial keratoplasty which replaces Descemet's and endothelium. It does not add stroma. |
|
The key difference between DSAEK and DMEK is that DSAEK adds stroma. Remember 'S' for Stroma.