There are lots of inheritance patterns and mutations which could potentially be tested, but only a few questions will appear in the exam. Therefore, we do not recommend you memorise this whole section but the highest yield content is discussed here for completeness.
Mitochondrial Inheritance
Mitochondria are maternally inherited through mitochondrial DNA, meaning only mothers can pass mitochondrial diseases to their children (both sons and daughters).
Kearns-Sayre syndrome
- Increased concentration of mitochondria in muscles
- Causes myopathy, ophthalmoplegia, ptosis, salt and pepper retinopathy and cardiac conduction defects
Leber Hereditary optic neuropathy
- Ganglion cell degeneration leads to optic atrophy.
- Presents predominantly in young men with progressive painless vision loss and a fundoscopic triad of pseudo-oedema, telangiectasia and tortuous vessels.
X-linked Recessive
Sons can be affected if the mother is a carrier of the mutation on one X chromosome, even if she shows no symptoms herself.
High Yield Conditions
- Congenital Retinoschisis
- Ocular Albinism
- Fabry Disease
- Lowe Syndrome
Autosomal Recessive
Important conditions include:
- Oculocutaneous albinism
- Stargardt's disease
Autosomal Dominant
Important conditions include:
- Congenital Cataracts
- Corneal Dystrophies
- Marfan Syndrome
- Stickler Syndrome: defective collagen 2 synthesis leading to an empty vitreous, retinal detachment (RD), deafness and systemic marfanoid and facial abnormalities.
- Neurocutaneous disorders: tuberous sclerosis, Von Hippel-Lindau and neurofibromatosis
Most of the potential exam questions fall into this category, so if in doubt during the exam - guess autosomal dominant.
Specific Chromosomes
Disease |
Chromosome |
|---|---|
Retinoblastoma |
13 (Rb1 gene) |
Stargardt's |
1 (ABCA4 gene) |
Aniridia |
11 (PAX6 gene) |
Myotonic dystrophy |
19 |
Marfan's |
15 |
Von Hippel-Lindau |
3 |
Retinitis pigmentosa |
3 (Rhodopsin gene) |
Coloboma
A coloboma is a hole in the structure of the eye, most commonly the iris. It is uncommon but high-yield in exams.
Optic Disc Coloboma
- Caused by a defect in embryonic fissure closure
- Associated with CHARGE syndrome
Lid Coloboma
Upper Lid
-
Upper lid coloboma occurs towards the medial half of the lid and is associated with Goldenhar syndrome
- This is a sporadic condition that features upper lid coloboma, limbal dermoids and maxillary hypoplasia
Lower lid
- Lower lid coloboma occurs towards the lateral half of the lid and is associated with Treacher Collins syndrome
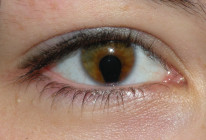
Iris coloboma
- The most common type
- Typically occurs on the inferotemporal aspect of the limbus
Limbal dermoids are congenital tumours which also occur on the inferotemporal aspect of the limbus