Pupil abnormalities present with anisocoria (unequal pupils).
Overview
Description |
Lesion |
Test |
|
|---|---|---|---|
Marcus-Gunn Pupil (Relative afferent pupillary light defect (RAPD)) |
In right RAPD: Light to the left eye will cause both eyes to constrict. Light to the right eye will not cause constriction, if the light is swung to the right, both eyes will be seen to dilate. The constricted pupil is the Marcus-Gunn pupil. |
Lesion of CN2 between the retina and the pretectal nucleus → light stimulus is not received. |
Clinical exam. |
Argyll-Robertson Pupil |
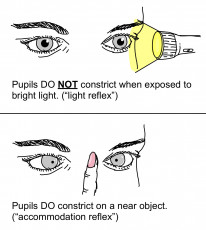
Bilateral irregular, miosis that does not react to light, but will accommodate (No constriction to light but will constrict to near objects). |
Lesion of dorsal midbrain affects light reflex pathway. Near reflex is ventral so is spared. Accommodative near reflex intact but light reflex is lost. |
Clinical exam. |
Adie's Pupil |
Unilateral dilated pupil that does not react to light and has vermiform iris border movements. The Adie pupil also gets smaller with time 'lil ole Adie'. The dilated pupil is Adie's pupil. |
Lesion of the post ciliary ganglion parasympathetic fibres. Initially there is no response to light or accommodation. With time, there is aberrant regeneration resulting in a hypersensitive near reflex. The light reflex is still lost. |
0.1% pilocarpine (very dilute) → Adie's pupil constricts due to denervation hypersensitivity. Treatment is with low dose pilocarpine to both eyes, causes denervation hypersensitivity constriction of the Adie's pupil and has no effect on normal pupil. |
Holmes-Adie syndrome is: Adie's pupil + decreased lower limb reflexes.
Horner Syndrome
Horner syndrome is a triad of: ptosis, anhidrosis and miosis. It is caused by a lesion in the sympathetic pathway to the head and neck. This pathway is outlined in detail on the principles of neuro-ophthalmology page.
Pathology
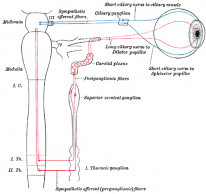
The lesion is classified according to which neuron is affected. Each of these is associated with characteristic aetiologies:
- First order: lesions of brain and spinal cord.
- Second order: Pancoast tumour and neck trauma.
- Third order: no anhidrosis. Caused by cavernous sinus lesions and internal carotid dissection.
In a third order Horner syndrome, there is no anhidrosis. This is because the secretomotor fibres that supply the sweat glands of the face leave this pathway before the third-order neuron. Therefore, a lesion of the third neuron will not affect sweat gland function.
Localising The Lesion
Administration of various topical medications bilaterally helps localise which order neuron is likely to be affected, and then relevant imaging of the high yield sites are conducted for diagnostics.
Topical Cocaine
- Used to confirm Horner syndrome, a lesion somewhere along the sympathetic chain.
- It blocks noradrenaline reuptake → enhances sympathetic effect and causes mydriasis in normal people.
- In Horner syndrome, the sympathetic pathway is broken so the Horner pupil will not dilate to Cocaine, but the normal one will.
Topical Apraclonidine
- Used to confirm Horner syndrome, a lesion somewhere along the sympathetic chain.
- Apraclonidine is an alpha agonist that causes mydriasis in normal people.
- In Horner syndrome, the sympathetic pathway is broken and the effector muscles at the end of the pathway are hypersensitive. When Apraclonidine is administered, the Horner eye dilates even more than the normal eye.
- The principle underlying this test is denervation hypersensitivity.
- Remember that medications are applied bilaterally, to both eyes.
Topical Hydroxyamphetamine
- Used to distinguish 3rd order lesions from the others (postganglionic or preganglionic). The ganglion in question is the superior cervical ganglion; it sits at the carotid bifurcation.
- Hydroxyamphetamine releases noradrenaline from the 3rd order neuron endings (postganglionic) to the dilator pupillae muscle which causes pupil dilation. If there is a 3rd order lesion, the pupil will not dilate. If there is no lesion, or a lesion of 1st/2nd order, the pupil will dilate.
Topical Dilute Adrenaline
- Used to distinguish 3rd order lesion from the others (postganglionic or preganglionic). The ganglion in question is the superior cervical ganglion; it sits at the carotid bifurcation.
- Adrenaline activates postsynaptic effector terminals to bring about the sympathetic response - pupil dilation. In Horner syndrome there is denervation hypersensitivity in these receptors, especially in 3rd order disease. If there is a 3rd order lesion, significant dilation is seen. Preganglionic Horner syndrome does not dilate as much.
Cocaine and Apraclonidine are used to diagnose Horner syndrome. Hydroxyamphetamine and dilute adrenaline are both used to localise 3rd order disease.
Painful Horner syndrome is carotid dissection until proven otherwise, so an urgent carotid angiogram is needed.

