The orbit is the bony socket that holds the eye and its associated structures.
Anatomy
Orbital openings

Optic foramen
- Found on the lesser wing of the sphenoid bone.
- Transmits the optic nerve and the ophthalmic artery.
Superior orbital fissure
- Lies between the greater and lesser wings of the sphenoid bone.
- Contains: Superior ophthalmic vein, lacrimal (CNV1) and frontal nerves (CNV1) and CN4.
- The structures within the superior orbital fissure and the common tendinous ring are: CN3, CN6, and nasociliary nerve (CNV1).
Inferior orbital fissure
- Lies between the maxilla and the greater wing of the sphenoid.
- Contains: infraorbital (CNV2) and zygomatic nerves (CNV2), and the inferior ophthalmic vein.
Retrobulbar anaesthesia affects all the nerves within the common tendinous ring (annulus of Zinn).
Bones of the Orbit
Bones |
|
|---|---|
Roof |
|
Medial wall |
|
Floor |
|
Lateral wall |
|
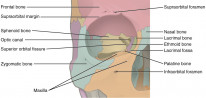
The medial wall is the weakest. It has a thin transparent membrane called the lamina papyracea through which infection can easily spread. This is how ethmoid cellulitis can lead to orbital cellulitis.
Clinical Manifestations
The eyeball can sit abnormally in the socket and this is the hallmark of orbital disease.

Exophthalmos
- Axial proptosis (straight out) indicates a lesion within the tendinous ring such as optic nerve glioma and cavernous haemangioma.
- Non-axial proptosis (protrusion at an angle) indicates a lesion outside the tendinous ring such as the lacrimal gland.
- Pseudoproptosis is the false appearance of proptosis and is typically due to facial anatomy.
Proptosis is the protrusion of any organ whereas exophthalmos is proptosis of the eye. The terms are used interchangeably in ophthalmology.
A Hertel exophthalmometer can be used to measure the degree of proptosis. >20mm indicates proptosis and any difference between the eyes should be investigated further.
Enophthalmos
Enophthalmos is the opposite of exophthalmos.
- Can be congenital as a result of atrophy of the ocular contents.
- Pseudoenophthalmos can be seen in a small eye (microphthalmos), ptosis or proptosis of the fellow eye.

