Optic Neuritis
Optic neuritis is inflammation of the optic nerve, anywhere from the chiasm to the optic disc. The most common cause is demyelination.
Pathology
Classification
- Papillitis: Inflammation of the optic disc. Typically presents in post-viral children with flame haemorrhages and an oedematous optic nerve.
- Retrobulbar neuritis: Disc is spared but the segment behind the eyeball is affected. The disc looks normal in this acute setting. More common in adults.
- Neuroretinitis: The disc and retina are both involved. Occurs in Lyme disease and cat scratch.
Disc Structure
- High myopes have larger discs and hyperopes have smaller discs.
- Axons travel within the neuroretinal rim of the disc, not at the centre. The centre of the disc is vascular and contains the central retinal vessels.
- Macular fibres are responsible for central vision and account for over 1/3 of the axons of the disc, this is why optic neuropathies commonly cause central/paracentral scotomas.
Cat scratch disease is caused by Bartonella Henselae and is transmitted by cats.
Diagnostics
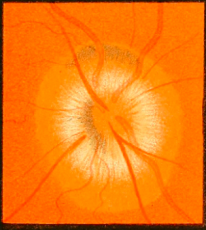
Typical Optic Neuritis
- Unilateral, decreased visual acuity (VA), loss of red-green colour and eye pain worse on movement.
- Typically affects 20-50-year-old women.
- It worsens over days and resolves within 2 weeks.
- Typical optic neuritis can be diagnosed clinically.
Atypical optic neuritis
- Atypical optic neuritis is when the features are not as above.
- It must be investigated further to exclude serious pathology such as space-occupying lesions.
The clinical manifestations of optic nerve disease are distinct from macular disease, and are commonly compared in questions.
Optic Neuropathy |
Maculopathy |
|---|---|
Loss of central vision and eye pain on movement |
Distortion of vision and loss of central vision |
Relative Afferent Pupillary Defect (RAPD) |
Hyperopic shift (see distance better) |
Red-green colour loss |
Blue-yellow colour loss |
Papilloedema
Papilloedema is swelling of the optic disc directly from raised intracranial pressure. Disc oedema is the generic term for a swollen optic disc.
Summary

- Papilloedema is a red flag sign that needs immediate investigation.
- Acute papilloedema causes an enlarged blind spot.
- Chronic papilloedema results initially in the loss of the inferior nasal quadrant of vision.
Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy (AION)
Ischemic damage to the optic nerve head is categorised as Arteritic or Non-arteritic.
Arteritic AION |
Non-arteritic AION |
|---|---|
Most commonly due to GCA |
Most commonly due to hypertension and diabetes |
Presents with a history of headaches and tenderness, sudden onset painful loss of vision unilaterally |
Sudden painless visual field defect unilaterally |
Disc is chalky white |
Focal swelling in segments of optic disc |
ESR elevated. Temporal artery biopsy is the best test but false negatives can occur because of skip lesions |
Treat the underlying cause and rule out GCA |
Initiate immediate Intravenous Methylprednisolone (IVMP) |
Multiple Sclerosis
MS is an important cause of optic neuritis and vision loss.
Pathology
T-cell mediated type 4 autoimmune neurodegenerative disorder of myelin in the central nervous system, which leads to inflammation and sclerosis.
Classification
- Relapsing remitting - Episodes of MS which come and go.
- Primary progressive - The episode lasts >1 year and gets worse continually with time.
- Secondary progressive - Like relapsing remitting but the baseline condition is worse after each episode.
Diagnostics
Presentation
- Classically presents in women in their 20s with optic neuritis.
Investigations
- Diagnosis is based on episodes of neurological dysfunction in the history alongside CNS lesions, disseminated across time and space respectively.
Other Optic Nerve Disorders
Pathology |
Presentation |
Investigations |
|
|---|---|---|---|
Leber Hereditary Optic Neuropathy |
Mitochondrially inherited disease, causing retinal ganglion degeneration |
Presents in young men with painless gradually worsening central scotoma, starting unilaterally. |
Fundoscopic triad of: pseudo oedema, telangiectasia and tortuous vessels |
Neuromyelitis Optica (Devic disease) |
Autoimmune episodic inflammation of the optic nerve and spinal cord |
Severe retrobulbar neuritis + transverse myelitis (causing muscle weakness and spasms) |
Associated with IgG antibodies against astrocytic aquaporin-4 |
Miller-Fisher Syndrome |
Variant of Guillain-Barré syndrome |
Characterised by a tetrad of: ataxia, areflexia, ophthalmoplegia and facial diplegia |
Associated with GQ1B auto-antibody |
Neuromyelitis Optica was first considered to be a subtype of MS but is classified as a unique disease identity today because it causes axonal damage as well as demyelination.

