An ectasia is a distension/dilatation of a section of a structure beyond its normal physiological dimensions. The cornea is a curved structure and corneal ectasia refers to abnormalities in this shape. On this page, the two highest yield ectasias are reviewed.
Keratoconus
Abnormal outward protrusion and thinning of a section of the cornea.
Pathology
- Progressive stromal thinning and apical coning of the cornea - exact cause is unclear.
- Abnormal shape of a section of the cornea leads to irregular astigmatism.
- Severe keratoconus can lead to tearing of Descemet's membrane and acute hydrops.
- There are many disease associations with keratoconus: Down syndrome, Marfan syndrome, retinitis pigmentosa, and Leber congenital amaurosis.
Keratoglobus is a globular ectasia as opposed to the conical ectasia in keratoconus. It tends to present more at birth and is associated with generalised corneal thinning.
Diagnostics
Presentation
- Typically bilateral and presents in adolescents.
- Munson sign - lower lid protrudes on downward gaze
- Vogt striae - corneal stromal striations seen on slit lamp
- Oil drop and scissor reflex on ophthalmoscopy
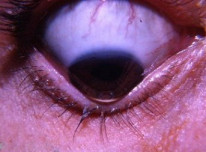
Keratoconus with Munson sign. By William Charles Caccamise, Sr, MD, CC BY-SA 4.0.
Investigations
- Steep keratometry readings.
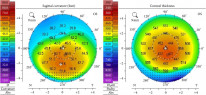
- Corneal topography (such as Pentacam) is used for diagnosis and monitoring.
Management (depends on severity)
- Mild (<48D of astigmatism) → Spectacles with cylindrical lenses
- Step up to rigid contact lenses and corneal collagen cross-linking (riboflavin drops and ultraviolet)
- Severe (>54D of astigmatism) → Keratoplasty
- LASIK is contraindicated because corneal thinning in keratoconus is unpredictable and you are unlikely to achieve any useful change in corneal shape with LASIK in these patients.
Corneal collagen cross-linking involves soaking the stroma in riboflavin (vitamin B2) followed by UV light exposure.
Pellucid Marginal Degeneration
Progressive thinning of the peripheral cornea, often inferiorly and bilaterally. This is a very rare disorder. There are two key things to know:
- Presents in adulthood with painless progressive bilateral blurring of vision over time.
- Corneal topography shows a characteristic butterfly pattern.

